Historical Overview and Key Trends
The Nikkei 225 index, a benchmark for the Japanese stock market, traces its roots back to 1949. Initially known as the Nikkei Dow Jones Average, it was established as a measure of the performance of 225 of the largest and most actively traded companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange.
The Nikkei 225, an index of the top 225 companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange, is a barometer of the Japanese economy. While it is not directly related to the some in france crossword , the Nikkei 225 can provide insights into the overall health of the Japanese economy and its potential impact on global markets.
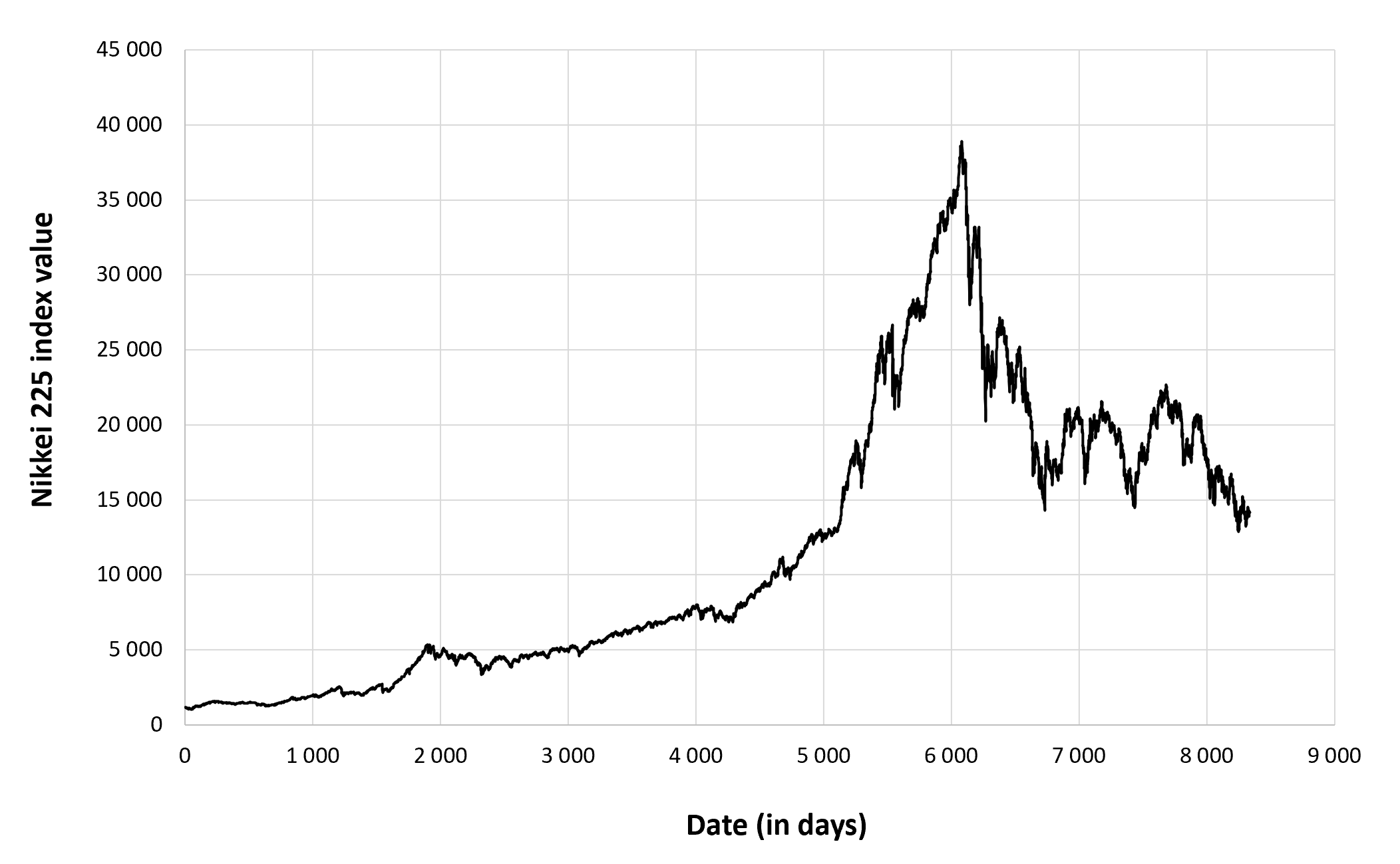
Over the decades, the index has witnessed significant events that have shaped its performance. The post-war economic boom of the 1950s and 1960s saw the Nikkei 225 soar, while the oil crises of the 1970s and the bursting of the asset price bubble in the early 1990s led to major downturns. The index reached its all-time high of 38,915.87 in December 1989, but it has since fluctuated, influenced by factors such as economic growth, corporate earnings, and global market sentiment.
The Nikkei 225 has been on a rollercoaster ride this year, but it’s still up over 10% since the beginning of January. The index has been boosted by strong earnings from Japanese companies and the Bank of Japan’s decision to keep interest rates low.
However, the index has also been weighed down by concerns about the global economy and the upcoming France vs Austria Euro 2024 match. Despite these concerns, the Nikkei 225 is still expected to finish the year in positive territory.
Long-Term Trends
Long-term analysis of the Nikkei 225 reveals several notable trends. The index has generally followed an upward trajectory over the decades, reflecting the growth of the Japanese economy and the increasing globalization of financial markets. However, the index has also experienced periods of volatility, with sharp corrections and prolonged downturns.
- Post-war Boom: The Nikkei 225 experienced a period of rapid growth in the post-war years, driven by the country’s economic recovery and industrial development.
- Bubble Economy: In the 1980s, the Nikkei 225 soared to record highs, fueled by speculative investment and rising asset prices. However, the bubble burst in the early 1990s, leading to a sharp decline in the index.
- Lost Decades: Following the collapse of the bubble economy, the Nikkei 225 entered a period of stagnation known as the “lost decades.” Economic growth slowed, and the index remained relatively flat.
- Recent Recovery: In recent years, the Nikkei 225 has recovered some of its lost ground, driven by factors such as quantitative easing and the weakening of the yen.
Composition and Sector Analysis

The Nikkei 225 index comprises 225 of the largest and most actively traded companies listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange’s First Section. These companies represent a wide range of industries, providing a comprehensive overview of the Japanese economy.
The index is heavily weighted towards large, established companies, with the top 10 constituents accounting for over 50% of its total market capitalization. These companies include blue-chip names such as Toyota, Sony, and Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group.
Sector Distribution, Nikkei 225
The sector distribution of the Nikkei 225 index reflects the dominance of the manufacturing sector in the Japanese economy. Industrial goods, including automobiles, electronics, and machinery, account for over 40% of the index’s weight. Other significant sectors include financials, consumer staples, and healthcare.
The index’s sector composition has a significant impact on its performance. For example, during periods of economic growth, cyclical sectors such as industrials and materials tend to outperform defensive sectors such as utilities and consumer staples. Conversely, during economic downturns, defensive sectors typically provide stability to the index.
Top-Performing Sectors and Companies
In recent years, the technology sector has been a major driver of growth for the Nikkei 225 index. Companies such as SoftBank Group, Tokyo Electron, and Keyence have benefited from the increasing demand for semiconductors and other electronic components. Other top-performing sectors include healthcare and consumer discretionary, driven by factors such as an aging population and rising consumer spending.
Economic and Market Factors: Nikkei 225
The Nikkei 225 is highly influenced by various macroeconomic factors and global economic events. These factors can significantly impact the index’s performance and investor sentiment.
Domestic macroeconomic factors such as GDP growth, interest rates, and inflation play a crucial role in shaping the Japanese economy and the Nikkei 225. Strong economic growth typically leads to increased corporate earnings and investor confidence, boosting the index. Conversely, economic downturns can negatively impact corporate profits and investor sentiment, leading to a decline in the index.
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by the Bank of Japan (BOJ) have a significant impact on the Nikkei 225. Low interest rates encourage borrowing and investment, which can stimulate economic growth and boost corporate earnings. On the other hand, higher interest rates can make it more expensive for businesses to borrow and invest, potentially slowing economic growth and negatively impacting the index.
Inflation
Inflation measures the rate of increase in prices for goods and services. Moderate inflation can be beneficial for the economy as it encourages spending and investment. However, high inflation can erode the value of investments and reduce consumer purchasing power, negatively impacting the Nikkei 225.
Global Economic Events
Global economic events, such as the COVID-19 pandemic or geopolitical conflicts, can significantly impact the Nikkei 225. These events can disrupt supply chains, affect consumer demand, and create uncertainty in the global markets. Such disruptions can lead to volatility and fluctuations in the index.
Relationship with Other Global Stock Indices
The Nikkei 225 is often compared to other global stock indices, such as the S&P 500 and the FTSE 100. While the Nikkei 225 primarily reflects the performance of the Japanese stock market, it is also influenced by global economic trends and market sentiment. Correlation and divergence between the Nikkei 225 and other global indices can provide insights into the relative strength and performance of different markets.
The Nikkei 225 index, a barometer of Japan’s economic health, has been on a rollercoaster ride in recent months. Amidst the volatility, investors have sought refuge in austria francia , a haven for safe-haven assets. While the Nikkei 225 remains a bellwether for Japan’s economy, it has also become a microcosm of the global economic landscape, reflecting the interplay of geopolitical tensions and market sentiment.
Nikkei 225, the leading stock index in Japan, is a barometer of the country’s economic health. Composed of the 225 largest publicly traded companies, it provides a comprehensive view of the Japanese equity market. For investors seeking exposure to the dynamic Japanese economy, the nikkei 225 offers a valuable investment vehicle, reflecting the performance of some of Japan’s most influential corporations.
The Nikkei 225, Japan’s primary stock market index, has been on a rollercoaster ride lately. Investors are keeping a close eye on Ben O’Connor , a financial analyst who has made some astute predictions about the market’s direction. O’Connor’s insights have been invaluable to many investors, and his opinions are highly respected in the financial community.
As the Nikkei 225 continues to fluctuate, investors will undoubtedly be paying close attention to O’Connor’s analysis for guidance.